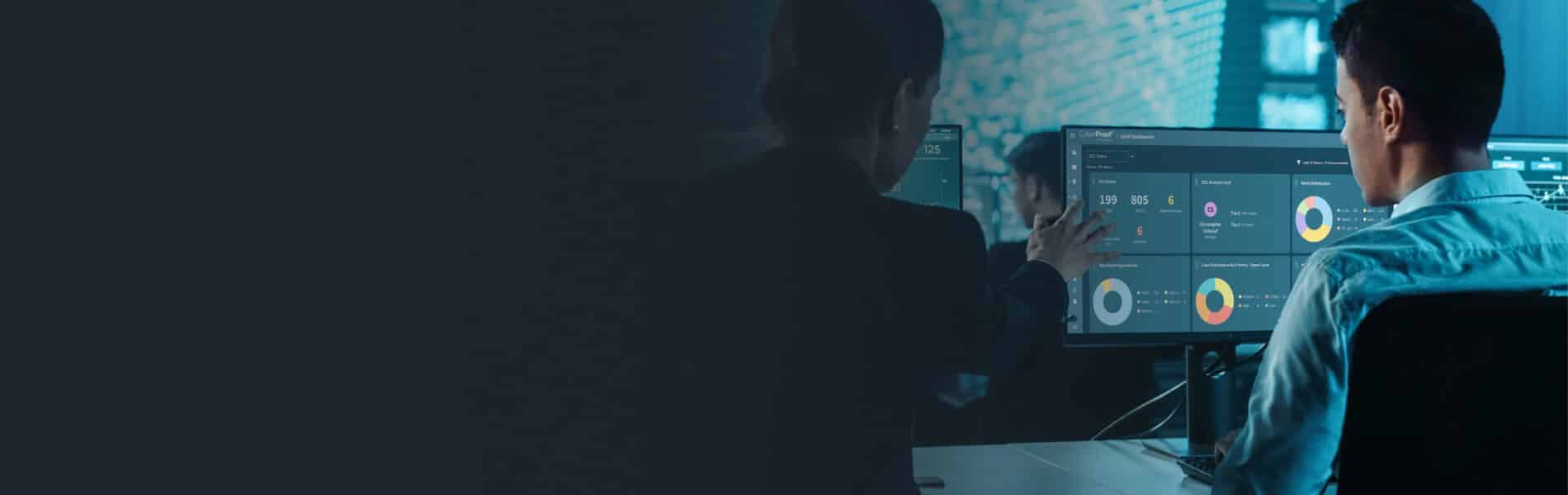
Today’s Cybersecurity Dilemma: Analyzing over 100,000 security incidents daily from more than 150 distinct threat actors
The Challenges:
- Security teams struggle to keep up with threats
- Uncertainty about relevant and significant threats
- Blind spots from ineffective, scattered cybersecurity tools

The Solution: Defend Against the Threats That Matter Most
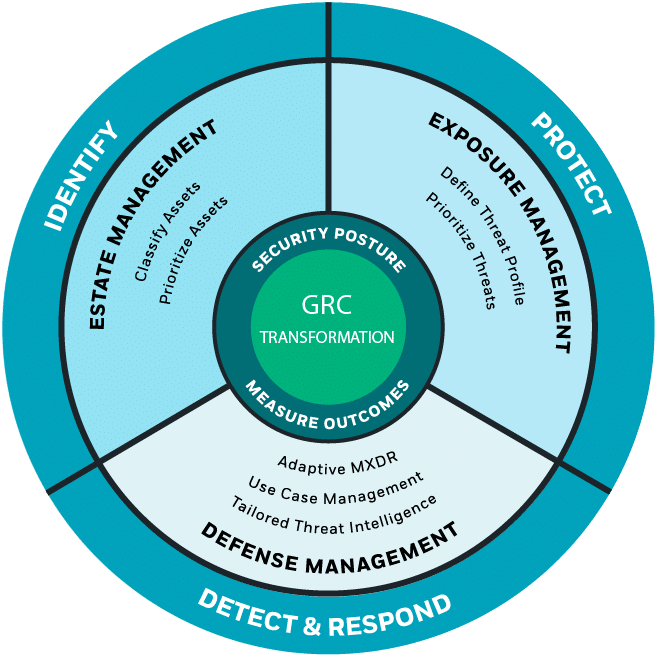
CyberProof provides an integrated threat-led platform that combines:
- Estate (Asset) Management: Tag, classify, and prioritize known and unknown assets to understand your exposure – continuously
- Exposure Management: Focus on relevant threats using CTEM and ASCA frameworks – continuously
- Defense Management: Optimize detection and response playbooks – continuously
- Resulting in GRC Transformation: Mitigate Global Risk, Define Business Outcomes & ROI, Mature Security Posture
Partners
“Today I have complete visibility into the entire environment, in real time”
Jamil Farshchi | Equifax CISO
Awards
Threat Alerts
Secure AI Development Environments — MCP Inspector Flaw Highlights Supply Chain Risks
Researchers have issued a warning about the potential for full system compromise through a vulnerability in Anthropic’s MCP Inspector tool — a popular open-source utility used by developers to test Model Context Protocol (MCP) servers. While a patch is available, this case highlights a wider risk: attackers can abuse poorly secured developer tools, local proxies, and open ports to escalate from simple web-based lures to full remote code execution.
Organizations adopting AI tools, agentic applications, or MCP frameworks should treat local development and testing environments as part of their attack surface. Validate that any MCP Inspector installations are updated to version 0.14.1 or later, review exposed network interfaces, restrict CORS settings, and apply strict least privilege. This serves as a broader reminder that open-source AI integration tools can introduce overlooked supply chain threats if not deployed securely.
Microsoft Patches 130 Vulnerabilities in July Update With Critical RCE and Zero Day
Microsoft’s July 2025 Patch Tuesday fixes 130 vulnerabilities, including 14 critical and 41 remote code execution flaws. Notably, it includes a publicly disclosed zero-day, CVE-2025-49719 (CVSS 7.5), an information disclosure bug in SQL Server that allows unauthenticated access to uninitialized memory over the network. Although exploitation is rated as “less likely,” the early disclosure increases risk. The most critical flaw, CVE-2025-47981 (CVSS 9.8), is a pre-authentication RCE in the Windows NEGOEX mechanism, posing a high risk of wormable attacks similar to WannaCry.
Other major fixes include RCE vulnerabilities in Microsoft Office and SharePoint (CVE-2025-49695 to CVE-2025-49704) and critical issues in Windows KDC Proxy, Connected Devices Platform, and Hyper-V components.