Cybersecurity Terms
- Alert
- Alert Observables
- Alert Triage
- Attack Map
- Attack Scenario
- Attack Scenario Elements
- BlackMamba
- Case File
- Cyber Incident
- Cyber Insider Threats
- Cyber Kill Chain
- Cyber Loss Occurrence
- Cyber Risk Elements
- Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI)
- Dark Web
- Data Hygiene
- Detection Control
- Dwell Time
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)
- Enriched Alert
- Event
- Event Detection System
- Fake News
- Impact Curve
- Incident Handling
- Incident Management Process
- Incident Recognition
- Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
- Intruder Hunting
- Investigation
- KPI or Key Performance Indicator and KRI or Key Risk Indicator
- Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attack
- Managed Detection and Response (MDR)
- Managed Security Service Provider (MSSP)
- MITRE ATT&CK
- Playbook
- Preventive Control
- Response Control
- Response Playbook
- (Actual) Response Time
- Response Window
- Runbook
- Sandbox Analysis
- Scenario Kit
- SCA or Service Capacity Agreements
- Security Event
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
- Security Operations Center (SOC)
- SLA or Service Level Agreements
- Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs)
- Threat Capability
- Threat Hunting
- Threat Potential
- Threat Technique
- Tor Browser
- Use Case
- Use Case Factory
- Vulnerability
What is an Alert
Definition
One or more events that correlate to a programmed alarm rule within a SIEM or other security management platform. Alerts are typically created through programmatic correlation logic within a SIEM. In the logical flow, events are correlated to create Alerts. Alerts are then Investigated to render either a False Positive or an Incident, and Incidents are then resolved through the Incident Response Process. Note that prior to being transitioned to an Investigation (or in some cases, after transition to Investigation), Alerts can be Enriched by queries to additional Event sources, non-event sources (such as systems logs, Threat Intelligence Services, AI Systems, Simulated Attack and Breach systems, Attack Surface Analysis systems, and Vulnerability Scanning systems), and historical data in a Data Lake.
Synonyms
Alarm; sometimes referred to as Investigations (although alerts are technically the trigger for the investigation, not the investigation itself); often improperly equated with Incidents.
What are Alert Observables
Definition
These are observed contextual elements of an Alert that can be used for formulating queries to other information sources in order to enrich the Alert.
The following are a few examples:
- The event’s IP address: The IP Address of an event reporting system is observed in the Alert and can be used to search other information systems that have logged related data for the system with that assigned IP address. This additional data serves to enrich the alert with supplemental context and aids in evaluating the Alert.
- The time of the activity that generated the Alert: This is an observable that can be used to search for other potentially related actions that occurred within a bounded time period (both before and after) the time of the Alert Event.
Synonyms
Event elements, event contextual data
What is Alert Triage?
Definition
This is the process of receiving a raw alert from a SIEM and conducting any required Alert Enrichment and investigation, to determine if the alert should be escalated to an Investigation for further review by Level 2 SOC staff or the customer or closed as a False Positive.
Synonyms
None
What is an Attack Map?
Definition
The probability map of the potential steps in an attack scenario for an attacker to achieve the anticipated objective. This concept is depicted below.
Synonyms
None
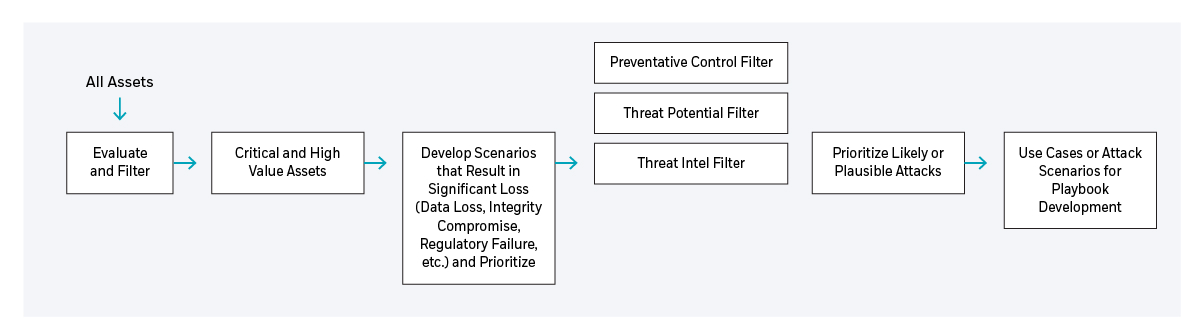
What is an Attack Scenario?
Definition
This represents the outcome of an attack, or the attacker’s desired outcome state for a specific Asset or set of Assets. While this outcome maps to the MITRE ATT&CK Matrix column titled Impact, it must be noted that an Attack Scenario describes a specific attack against a specific Asset or set of Assets and can therefore be mapped directly to a loss valuation.
Further, as Attack Scenarios are human driven, they may have more than one outcome state, and may shift in desired outcome at any point in the attack. Attack Scenarios are part of the Use Case Development Cycle, as depicted below, in a traditional Risk Management process. This process includes the following:
- Start with the input of all assets.
- Filter that to Critical and High Value Assets.
- Develop a list of scenarios that result in significant loss (data loss, integrity compromise, regulatory failure, etc.), and prioritize based on damage to the organization.
- Screen or validate against threat intelligence information, threat potential (do the tools exist to conduct the attack), and preventive controls in place, and refine to a list of likely attacks for use in the playbook development cycle.
Synonyms
None
What are Attack Scenario Elements?
Definition
These map directly to the MITRE ATT&CK Matrix Column titles of Initial Access, Execution, Persistence, Privilege Escalation, Defense Evasion, Credential Access, Discovery, Lateral Movement, Collection, Command and Control, Exfiltration, and Impact. While not all Elements will be present in every Attack Scenario, some combination of these must be present for the attack to be successful. For example, there must be some form of Initial Access, Execution, and Impact, at a minimum.
Synonyms
Cyber Kill Chain
What is BlackMamba?
Definition
An AI-related Proof of Concept (PoC) created by a security team to explore and illustrate the potential impact of generative AI.
What is a Case File?
Definition
One or more Alerts, Investigations, or Incidents that are in some way related.
Synonyms
None
What is a Cyber Incident?
Definition
In the context of Cyber Security, an Incident represents a confirmed malicious action by a Threat Actor. Logically, an event or set of correlated events can trigger an Alert, indicating that there is suspicious activity that could represent the malicious activities of a threat actor. When an Alert is Investigated, it can be de-escalated to a False Positive, or escalated to an Incident. Once escalated, the Incident can be resolved through the Incident Management Process.
Synonyms
None
What are Cyber Insider Threats?
Definition
Insider threat actors can include people who are currently employees and those who used to be employees – as well as “outsiders” with access to an organization’s internal environment, such as contractors, vendors, and suppliers.
Generally, an attack by an insider falls into one of the following categories:
- Negligence – Someone who compromises data by mistake, generally due to bad cyber hygiene
- Malicious Intent – Someone who compromises data purposely or exfiltrates confidential information to sell to third parties (e.g., for business intelligence or insider trading)
- Infiltration – A compromised account or system, i.e., someone whose account was taken over by a bad actor and misused, or a system that was compromised
Synonyms
Attack Scenario, Attack Scenario Elements
What is the Cyber Kill Chain?
Definition
The Cyber Kill Chain defines the different stages of a cyber attack. It is widely used by the cyber security community to map out the key activities an adversary must complete to reach their objective and improve detection of the relevant tactic, techniques and procedures (TTPs) used in that process.
The Cyber Kill Chain consists of the following seven stages:
- Reconnaissance – Collecting information to better understand the target.
- Weaponization – Using a backdoor and exploit to build a deliverable malware payload.
- Delivery – Delivering the payload to the target (e.g., email with malicious link).
- Exploitation – Executing the code on the victim’s system to exploit a vulnerability.
- Installation – Installing malware on the system and backdoor to allow persistent access.
- Command and Control – Creating a channel to remotely control the target system.
- Actions and Objectives – Attacker achieves their goal (e.g., data exfiltration, disrupting operations, etc.).
Synonyms
None
What is a Cyber Loss Occurrence?
Definition
The loss resulting from an Attack Scenario.
Synonyms
Impact in the MITRE ATT&CK Matrix
What are Cyber Risk Elements?
Definition
The factors that influence Cyber Risk – Threat Capability, Actor Intent, Preventive Control Strength (inversely, Vulnerability), Detection Control Strength, and Response Control Strength. For each attack scenario, these five factors can be used to calculate the probability of attack scenario success, or risk.
Synonyms
Risk Factors
What is Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI)?
Definition
Cyber threat intelligence (CTI) has become a near-universal component of modern cyber security strategies. Compared to generic insights about emerging attack vectors, targeted threat intelligence gives teams the intelligence necessary to pre-empt and neutralize attacks before they can harm your business.
Synonyms
None
What is the Dark Web?
Definition
The dark web requires the use of an anonymizing browser called Tor in order to be accessed. It is a part of the Internet that is not visible to search engines. The dark web is World Wide Web content that is on darknets – i.e., computer networks that use the Internet but cannot be accessed unless the user has the necessary software, configuration, or authorization.
Synonyms
None
What is Data Hygiene?
Definition
In cyber security, data hygiene refers to the basic cyber security issues that security leaders need to bear in mind, in order to protect their organizations and their data from a breach.
Synonyms
None
What is a Detection Control?
Definition
A control (access logging, network monitoring, AAA logging, anomaly detection, malware detection, config monitoring, etc.) designed to detect a potentially malicious action within a given environment. Typically, these detection capabilities map to a specific Threat Technique. However, in the case of anomaly detection, they reflect only the fact that something out of the normal occurred. For each Attack Type, and each step (Threat Technique) within the Kill Chain of the attack there may be Detective Controls that would alert the organization that a Threat Agent is actively engaged in an Attack Process. It should be noted that Detection is functionally an input to Response. Obviously, no person or system can respond to that which was not first detected.
Synonyms
None
What is Dwell Time?
Definition
The length of time a hacker goes undetected after breaching the first-line security and gaining access to the network.
Synonyms
None
What is Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)?
Definition
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) is a powerful tool that provides organizations with both endpoint protection and advanced investigation and threat hunting capabilities. EDR comes with a default set of behavioral detection rules that are created by high-level research teams and provide endpoint protection from day one.
Synonyms
Managed Detection and Response (MDR)
What is an Enriched Alert?
Definition
These are Alerts that have been Enriched by the addition of context information typically derived through queries to supplemental Event sources, non-event sources (such as systems logs, Threat Intelligence Services, AI Systems, Simulated Attack and Breach systems, Attack Surface Analysis systems, and Vulnerability Scanning systems), and historical data in a Data Lake.
Synonyms
None
What is an Event?
Definition
A human, end-system, or network security related, activity that is identified and recorded in some way.
Synonyms
None
What is an Event Detection System?
Definition
Any system, appliance, device, or software that can generate a security record based on some user, external system, or network activity that can be forwarded to a SIEM. Operating systems, applications, and event detection systems can all be event detection systems. The method of detection can be content, condition, activity (or change), or anomaly based.
Synonyms
None
What is Fake News?
Definition
Fake news, also known as junk news, hoax news, pseudo-news or alternative facts, is a broad term, covering a variety of techniques used by threat actors that can include:
- Incorrect content – Fake text written to incriminate someone or spread an inaccurate report.
- Photoshopped images – Photographs that were falsified, presenting a picture that is far from the truth.
- Fake footnotes – Artificially created footnote links that lead to fake sources; these give credibility to the content’s alternative facts.
- Clickbait – A technique through which a threat actor earns money by enticing victims to click on a fake link; the link – the “headline” of the fake news article – is written in a style designed to make it very attractive to readers.
- Clickjacking – A technique that tricks victims into downloading something dangerous; it allows threat actors to take control of the victim’s computer or to steal personal information. As in clickbaiting, the link – the “title” of the fake news article – is written in a style designed to make it very attractive to readers.
Synonyms
None
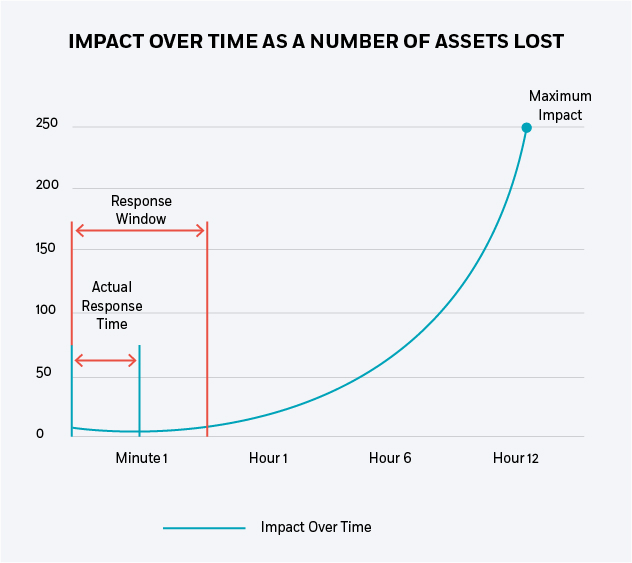
What is the Impact Curve?
Definition
The Impact Curve represents the amount of Loss or Damage over time from the point in time where an Attack Scenario was potentially detectable to the point where the attack would have caused its maximum potential Loss or Damage had it gone completely unchecked. See the following graphic for an explanation of the relationships between Impact Curve (IC), Response Window (RW), and Actual Response Time (ART).
Synonyms
None
What is Incident Handling?
Definition
Incident Handling is a set of actions that consist of detecting, reporting, assessing, responding to, dealing with, eradicating, and learning from security incidents.
Synonyms
Incident Management Process
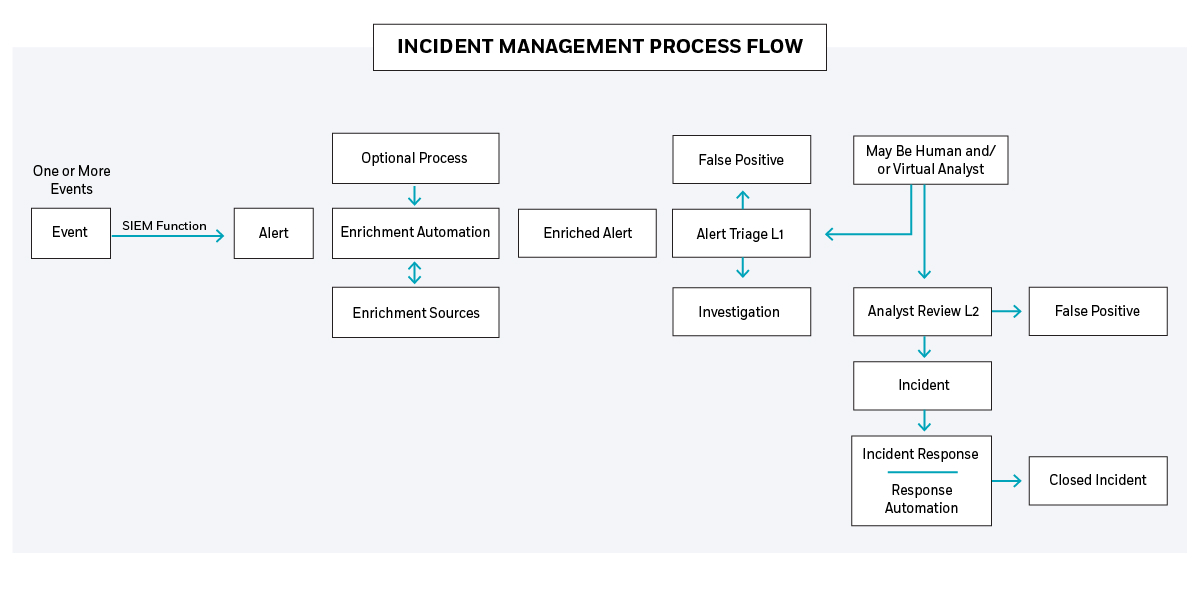
What is the Incident Management Process?
Definition
Incident Management defines the workflow for handling detected Events. This process is depicted in the diagram below and includes Event Correlation and Processing, Alert Creation, Alert Enrichment, Alert Triage, Investigation Analyst Review, and Incident Response.
Synonyms
Incident Handling
What is Incident Recognition?
Definition
The act of identifying the cause of an Investigation to be a confirmed malicious activity by a Threat Actor. Incident Detection is therefore the escalation of an Investigation to Incident status. Note that all Incidents begin as one or more Events that are correlated into an Alert, which is then escalated to an Investigation, and then further escalated to an Incident.
Synonyms
Incident Detection
What are What are Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)?
Definition
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) are pieces of forensic data that identify potentially malicious activity on an information system or network that serve as useful information for detecting intrusions on a system or network, such as data breaches and malware infections.
Synonyms
None
What is Intruder Hunting?
Definition
Intruder Hunting is a process for aggressive intruder detection and eviction, focused on specific targeted assets. Threat Hunting is often confused with Intruder Hunting. For example, performing detective work to identify anyone considering committing a burglary in your neighborhood would be Threat hunting, while setting up detection sensors and traps within your home is Intruder Hunting. Threat Hunting therefore is generally external (looking for threats against the organization), while Intruder Hunting is internal (looking for threats that have potentially breached the organization’s defenses).
Synonyms
None
What is an Investigation?
Definition
In the context of Cyber Security, an Investigation represents a probable malicious attack by a Threat Actor. Logically, an event or set of correlated events can trigger an Alert, indicating that there is suspicious activity that could represent the malicious activities of a threat actor. When an Alert is Triaged, a preliminary determination is made that the Alert is either a false positive, or a probable malicious action that warrants further investigation. If so, the Alert is transitioned to Investigation status and is escalated to a Level 2 SOC analysts for further review. During the SOC Level 2 review, the Investigation can be de-escalated to a False Positive, or escalated to an Incident. Once escalated, the Incident can be resolved through the Incident Management Process.
Synonyms
Escalated Alert, Probable Attack
What are KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) and KRIs (Key Risk Indicators)?
Definition (In the context of a Security Service)
A KPI is intended to quantify the Effectiveness or Efficiency of a service. KPIs tend to measure Accuracy, Capacity, Time to Complete (an activity), and Improvement of Performance. While it is appropriate to pre-define performance baselines that will set the expectations for performance, KPIs are most useful and applicable when used in the context of trending over time. In this regard, KPIs should have two thresholds – the first being the expected level of performance, and the second being a lower bound that serves as an indicator of a potential issue, or KRI (Key Risk Indicator). By leveraging this multi-threshold approach to performance measurement, separate sets of measurement do not need to be maintained and tracked for KPIs and KRIs, since they are simply different performance boundaries within the same metric.
Synonyms
Performance Metrics
What is a Large Language Model (LLM)?
Definition
Large language models (LLMs) are artificial intelligence systems that have been trained on extensive amounts of text data. Through this training, they learn patterns, context, and complexities of human language. They can understand and generate text that mirrors human communication, with capabilities including answering queries, drafting detailed essays, translating between different languages, or writing creative content such as stories and poems. These models can adapt to diverse language tasks, making them powerful tools for many applications in today’s digital world.
What is a Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attack?
Definition
Millions of accounts are currently vulnerable to a cyber security threat known as Password Reset Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks – a form of attack that allows even a relatively unsophisticated attacker to take over user accounts by exploiting poorly designed password reset procedures.
In these attacks, the attacker creates a malicious website, where victims “register” to receive free services, software, or a free download. When the victim starts entering personal information, the attack begins. The attacker uses the information provided during registration to take over a victim’s account on other websites.
Synonyms
Attack Scenario, Attack Scenario Elements
What is Managed Detection and Response (MDR)?
Definition
MDR services help organizations reduce cyber risk by proactively detecting and responding to validated incidents, leading to a continuous reduction in response time and associated exposure risk.
Organizations seeking MDR services should evaluate the provider’s ability to provide proactive threat hunting based on their needs, as well as their approach to gaining both the depth and breadth of visibility. Organizations should also seek providers who can demonstrate comprehensive response options.
Synonyms
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)
What is a Managed Security Service Provider (MSSP)?
Definition
A Managed Security Service Provider (MSSP) allows you to outsource the management of your security technologies, operations, event monitoring and/or Incident Response services – and sidestep the logistical, financial and resource challenges of maintaining 24×7 security operations in-house.
Synonyms
None
What is MITRE ATT&CK?
Definition
The MITRE ATT&CK is a comprehensive matrix of tactics and techniques that provides organizations with a way to develop, organize, and use a threat-informed defensive strategy that can be communicated in a standardized way.
The goal of the MITRE ATT&CK is to be a living dataset that is continuously evolving – updated with new threat information on a continual basis. It is a framework that organizes known cyber threats, and categorizes the activities of malicious actors in terms of their Tactics, Techniques and Procedures (TTPs).
A technique is a unique method identified by MITRE of achieving a specific tactic, which is an intrusion goal. For example: Privilege Escalation is listed as a tactic, while AppCert DLLs is a technique to achieve it.
For each technique listed in the MITRE ATT&CK, the following information is provided:
- An identifier
- Tactic that it’s associated with
- Platform it’s applicable to
- System or permission requirements
- Defense strategies bypassed
- Data sources that identify use of the technique
- Mitigations and detection methods
Synonyms
Attack Scenario, Attack Scenario Elements
What is a Playbook?
Definition
A process flow documented within the CyberProof Defense Center that defines the steps involved in the response actions for a specific Alert or Alert Type. Some or all of the process may be automated. This is similar to a Runbook in that it is also a process flow; but it is not the same in that a runbook is a written document that tells the customer how to respond to a scenario and interact with the SOC.
Synonyms
Response Script, Automation Script
What is a Preventive Control?
Definition
A control (software patch, network filter, authentication process, access control, etc.) designed to prevent a specific Threat Technique. For each Attack Type, and each step within the Kill Chain (Threat Technique) of the attack there may be Preventative Controls that would Prevent the Threat Agent from successfully completing that defined step in the Attack Process.
Synonyms
None
What is a Response Control?
Definition
This control represents the loss mitigation measures that can be put in place to halt or disrupt an attack and terminate the line of the Impact Curve. Typically, this is done by altering the course of the attack, engaging secondary Preventative Controls to prevent the next Threat Technique or step in the attack, or limiting the impact and extent of loss though some form of loss recovery (backups, for example).
Synonyms
Incident Response Action
What is a Response Playbook?
Definition
A response playbook is a series of steps or procedures documented and used for responding to Security Alerts or Incidents. These can be manual, fully automated or a hybrid of both.
Synonyms
None
What is Actual response Time?
Definition
This is the time delay from initial Event Detection, through correlation, Alerting, Investigation, Incident Creation, until an Incident is resolved, and loss mitigation measures are put in place to halt the attack and terminate the line of the Impact Curve.
Synonyms
None, but term is misused frequently.
What is the Response Window?
Definition
This is the time period starting at attack inception or initiation until an Attack Scenario results in unacceptable loss or damage to the organization.
Synonyms
None
What is a Runbook?
Definition
A document that details the customer interaction processes with the CyberProof SOC for a specific scenario or set of scenarios. The document focuses on the steps each organization will take to collaborate and defines what actions are expected from all participants. It is different than a Playbook that defines incident response processes that may be partially or completely automated.
Synonyms
Playbook
What is Sandbox Analysis?
Definition
Sandbox analysis is used to test new code and to test software that is potentially malicious. A sandbox is an isolated testing environment in which users can conduct activities (running programs, executing files) without having an impact on the environment in which they run.
Synonyms
None
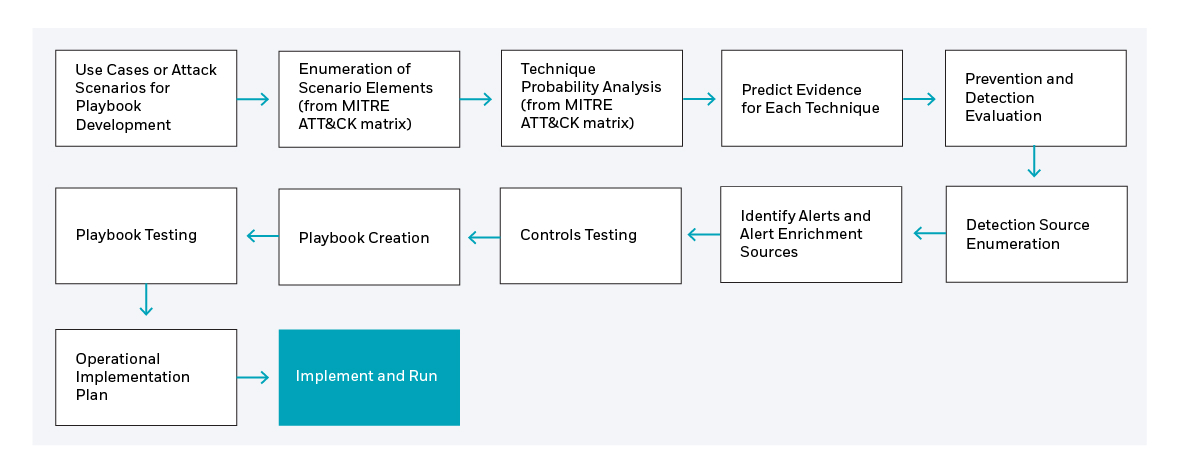
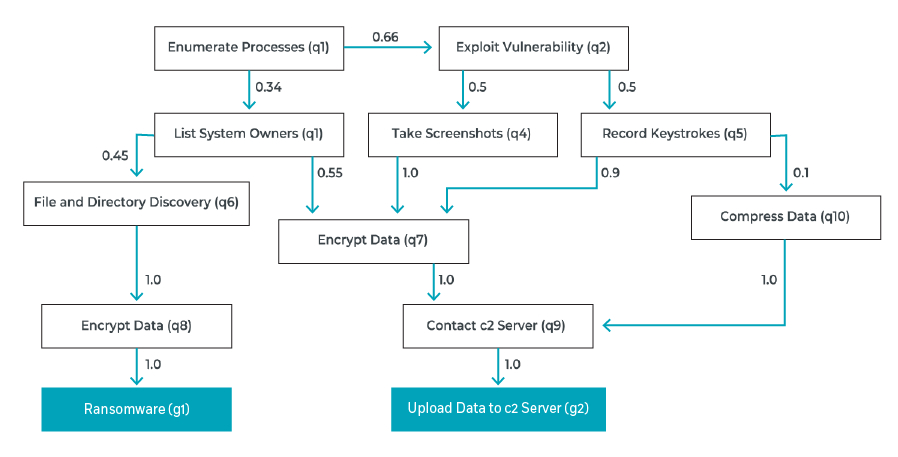
What is a Scenario Kit?
Definition
The Scenario Kit is the product of the Scenario Development Cycle. Each approved Attack Scenario will result in a Scenario Kit. This cycle includes the development of an Attack Scenario (including the Risk Analysis Report associated with the scenario), the Scenario Element Enumeration Process, the Technique Probability Analysis, Evidence Prediction, Prevention and Detection Evaluation, Detection Source enumeration, Identify Alerts and Alert Enrichment Sources, Controls Testing, Playbook Creation, Playbook Testing, and Operational Implementation Plan. Therefore, the Kit includes all documentation, code, algorithms, and automation resulting from the execution of each of the process steps identified above. The process flow below depicts Scenario Kit development after the creation of the Attack Scenario.
Synonyms
None
What are Service Capacity Agreements (SCAs)?
Definition
An SCA defines the capacity limits of a service to be provided. These capacity bounds are required for meaningful SLAs (see SLA below), in that they indicate the quantities of service to which the SLAs are applicable.
Synonyms
None
What is a Security Event?
Definition
A human, end-system, or network security related activity that may be identified and recorded via a logging mechanism.
Synonyms
None
What is Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)?
Definition
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) software provides a platform for collecting logs and event data – helping organizations identify and investigate threats.
A next-generation SIEM aims to provide cloud-scalable security information and event log management. Using this kind of SIEM, customers can aggregate data across the enterprise from all sources, including users, applications, servers, and devices running on-premises or in any cloud – allowing the review of millions of records in a few seconds. A next-generation SIEM can also generate high-context alerts – reducing false positives and prioritizing escalations.
Synonyms
None
What is a Security Operations Center (SOC)?
Definition
The Security Operations Center (SOC) leverages people, processes, and technology to monitor a company’s networks, devices, appliances, information stores, and more. The SOC is a physical or virtual space, where all security events logged by a company are correlated. The SOC’s analysts use the technology and develop processes that determine how to manage and respond to events – continuously monitoring, detecting, and responding to threats to ensure the full security coverage of the organization by.
Synonyms
None
What are Service Level Agreements (SLAs)?
Definition (In the context of a Security Service)
An SLA is used to measure the conduct of a service provider in the execution of a service contract.
This includes what was done in the execution of duties as well as the time that is expected for the completion of specific tasks within the context of an agreed capacity.
Therefore, SLAs generally define “What” service is to be provided and “When” or “How much Time” it will take to provide a service, whereas the Service Capacity Agreement defines “How Much” of the service is provided.
For example, if the time to process an alert or investigation is quantified, this time requirement must be linked to a capacity of the service such that it is applicable only up to a specific number of alerts in a given period of time.
In other words, this time requirement must be limited by an agreed capacity of the service. These capacities or at least SLA application boundaries are typically defined in the Service Capacity Agreement.
For example, if the agreed service capacity is 20 alerts per hour, then there can be an SLA in place that states each alert is processed within 30 minutes for up to 20 Alerts per hour.
If an unexpected and wide-ranging attack generates 500 alerts within an hour, the SLA can only apply to 20 of those alerts given that 20 alerts per hour is the agreed service capacity.
It is critical that all time-bound SLAs are mapped to service capacity as SLAs have financial penalties for the provider, and must therefore represent actions within the provider’s control.
As an additional example in the application of context around an SLA, consider an SLA that provides a 2-hour response time to implement countermeasures to a detected attack.
While this may be a reasonable expectation for a known attack or malware variant, it may not be reasonable for a new attack type or never-before-seen malware, where extensive effort may be required to reverse engineer the attack to determine an effective countermeasure.
Note that while SLAs are a good tool for ensuring standards of practice, KPIs are far better for managing performance and performance improvement.
Synonyms
None
What are Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs)?
Definition
Tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) allow cyber security experts to analyze threat actors, attack patterns, and how the attacks are orchestrated. Tactics are the highest-level description; techniques are more detailed (within the context of a tactic); and procedures are even lower level (within the context of a technique).
Synonyms
None
What is a Threat Capability?
Definition
Threat Capability is a measure of the probability that an adversary has the ability and interest to launch a damaging attack against an organization.
Synonyms
Adversary Capability
What is Threat Hunting?
Definition
This is the use of Threat Intelligence gathering techniques to identify potential Threat Actors, Threat Techniques, Exploits, Attack Campaigns, and geopolitical situations that may pose a threat to the target organization.
Threat hunting is critical in providing visibility into threats that may have bypassed an organization’s perimeter controls. It allows you to leverage both security and non-security related information, and to supplement wide coverage with more in-depth investigation.
Synonyms
None
What is a Threat Potential?
Definition
Threat Potential can be represented as Threat Capability (TC) minus Control Strength (CS) for a given Threat Technique (TTn) or TP(TTn) = TC(TTn) – CS(TTn). A complete mapping of Preventative Controls to known Threat Techniques identifies which attacks have the potential for success, and links specific Preventative Control Gaps to defined Risks.
Synonyms
None
What is a Threat Technique?
Definition
A specific technique employed during a cyber-attack. This specific technique may be a component within one or more Attack Scenario Elements (also known as a Cyber Event Chain or Kill Chain). Each technique is preventable or detectable through some method, but since several Attack Scenarios may have combinations of overlapping Threat Techniques, identification of the correct associated Attack Scenario may not be possible with only one or two detected Threat Techniques. In the MITRE ATT&CK Matrix, each of the items under the categories of Initial Access, Execution, Persistence, Privilege Escalation, Defense Evasion, Credential Access, Discovery, Lateral Movement, Collection, Command and Control, and Exfiltration represents a Threat Technique.
Synonyms
Threat Action, Threat Event, Attack Technique. Note that Attack Step and Kill Chain Step are frequently but incorrectly used to describe this action, in that a kill chain step is a step in the kill chain model, while a Threat Technique is a specific technical action that fulfills that step in the model sequence. There may be several Techniques that accomplish the same outcome.
What is a Tor Browser?
Definition
Developed by the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory for military purposes to anonymize emails, today the Tor Browser is the most popular software available for browsing the Internet anonymously. It is free, effective, and does not require very much technical knowledge to set up.
Tor is built as a modified version of the Firefox browser. It uses Onion routing, which is a scheme based on layered encryption, to hide TCP traffic. By default, it enables continuous private browsing mode.
Tor hides information such as the user’s activity and location from entities conducting network surveillance or doing traffic analysis.
Tor’s anonymity traits make it popular among journalists, whistleblowers and political dissidents and make it attractive to malicious actors, as well. In fact, Tor has become one of the keys to accessing the Dark Web.
Synonyms
None
What is a Use Case?
Definition
Use Cases represent specific techniques that produce undesirable outcomes. Once this undesirable outcome is identified, a prediction is made as to the evidence that would indicate the undesirable activity has occurred, is occurring, or is about to occur. Typically, this evidence is expressed as an Alert Rule within the SIEM that maps the evidentiary events to the named outcome and creates an Alert to allow the organization to take the appropriate action. The example below illustrates these relationships:
A few examples below illustrate these relationships
Use Case – Persistent Malware Infection: Evidence – A specific Malware has been detected multiple times over a long period of time (more than 4 days)
- Events –EDR detection of Malware a compute platform
- Alert Rule – The same variant of malware is detected on one or more systems over a 4-day period
- Alert – an alert is triggered bearing the same name as the Use Case.
Use Case – Discovered Vulnerability: Evidence – A High and critical vulnerabilities on critical servers requires immediate remediation.
- Events – A vulnerability Scanning system detected a high rated vulnerability on a critical server and created an event.
- Alert Rule – This single event triggers an alert.
- Alert – an alert is triggered bearing the same name as the Use Case and invokes a Playbook to create a remediation ticket in the ticketing system.
Synonyms
None
What is a Use Case Factory?
Definition
The Use Case Factory defines a process that includes the following general steps:
- Convert Negative Outcome Scenarios into Attack or Action Scenarios (i.e., how would the outcome happen). This process typically incorporates input from threat intelligence sources, penetration testing, and vulnerability assessments.
- Extrapolate from the Attack Scenario the specific Attack Technique or Techniques required to perpetrate the attack or unwanted scenario.
- Identify the evidence that would be generated by the technique or techniques.
- Identify the data sources and mechanisms required to detect such evidence.
- Define Preventive and/or Response Controls to be engaged upon detection of evidence.
- Implement necessary data source logging and create detection correlation rules, if needed, to create an Alert upon detection.
- Implement Prevention or Response controls.
- Test, Implement and operationalize the Detection control and the associated Prevention or Response controls.
Synonyms
None
What is a Vulnerability?
Definition
Weakness in system/application. Vulnerabilities are typically rated via a CVSS score (Common Vulnerability Scoring System) which is an open industry standard for assessing the severity of computer system security vulnerabilities. The score assigns a severity or risk rating to vulnerabilities, allowing responders to prioritize responses and resources according to threat. However, more advanced Vulnerability Management Systems also take into account other risk factors such as the availability of an exploit against the vulnerability, frequency of exploit usage, the criticality of the vulnerable system, Attack Surface Analysis that can determine the accessibility of the vulnerable system from potential attackers.
There are also multiple classifications of vulnerabilities such as the following:
- Unknown or Zero Day Vulnerability. These are vulnerabilities that are unknown to the manufacturer of the system or software, and to the makers of prevention systems, yet may be known by a small number of researchers or hackers. There is generally little to no defense against exploits of these vulnerabilities other than AI based predictive analytics or anomaly detection systems.
- Known but Unpatched Vulnerabilities. These are vulnerabilities that are widely known and for which the manufacturer has created a working update or “patch”. However, that patch has not yet been applied to the systems that have this weakness. These systems are therefore still vulnerable in spite of the availability of the corrective updates. This is not uncommon in that sometimes the patch causes malfunctions in other software on the vulnerable platform, and this other software is critical to business operations. In these cases, it is essential to create filtering or protective mechanisms to block the exploit on its path to the vulnerable system.
- Patched Vulnerabilities, although a seemingly oxymoronic term, given that a patched system is no longer vulnerable, is a legitimate term within the Vulnerability Management Process that indicates that patching remediation has been performed on a given system or set of systems.
Synonyms
None