What is XDR? (Extended Detection and Response)
What does XDR stand for? XDR is an acronym for eXtended Detection & Response, and it is a security strategy that involves collecting, correlating and proactively analyzing a wide range of data to isolate and mitigate security threats.
In this guide, we will answer questions like:
- What is XDR security?
- How has XDR technology evolved over time?
- How can today’s organizations benefit from incorporating XDR as part of their security strategy?
How is XDR different from existing solutions?
To understand the question “what does XDR mean?” – it’s important to consider the evolution of cybersecurity solutions over time.
How does XDR compare to EDR or MDR?
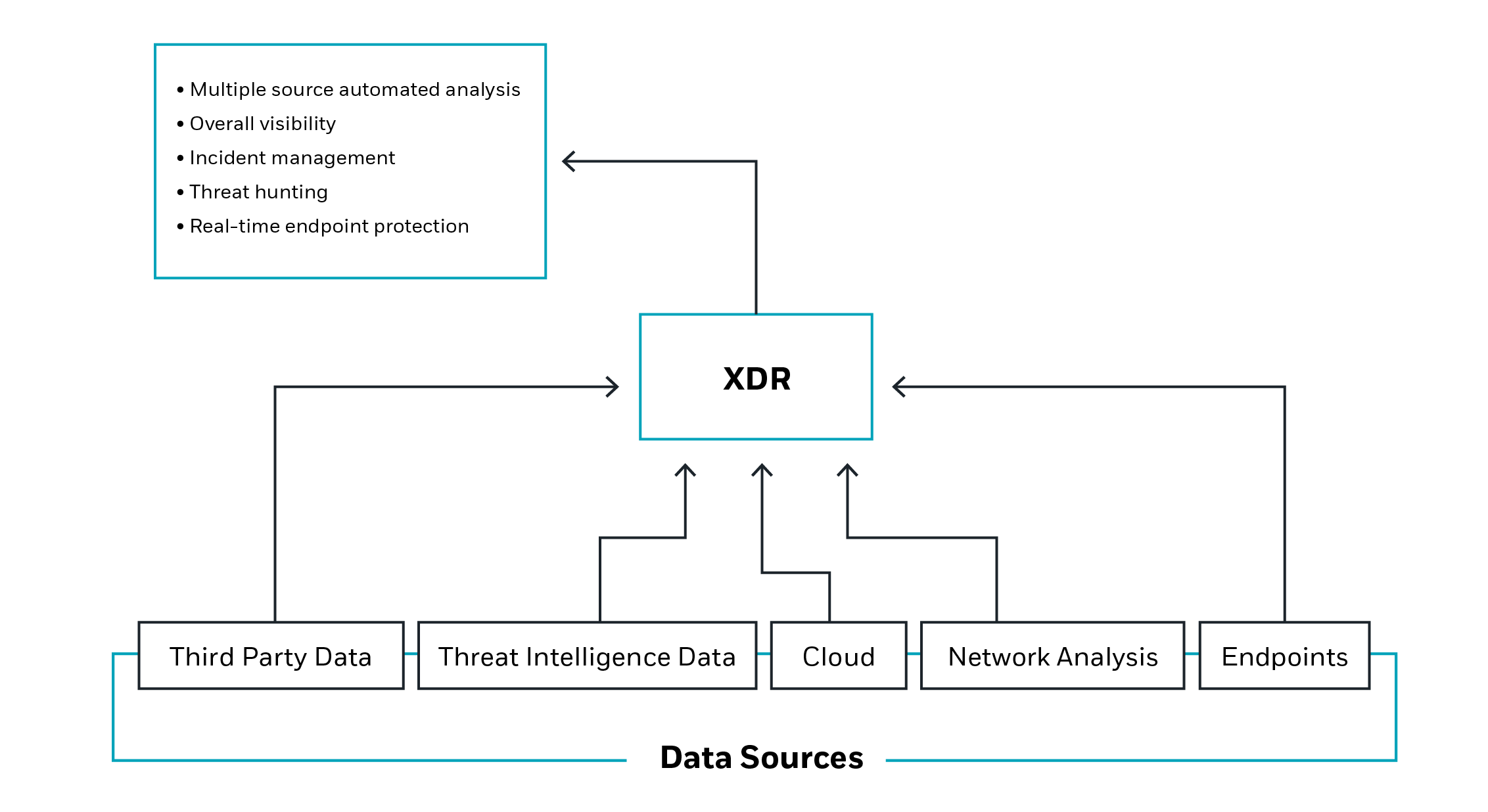
While EDR focuses on endpoints and end-user assets, XDR encompasses a wider range of data, such as information from the network, from security logs, or from the cloud. Cloud-native XDR can aggregate a wide range of data into a single consolidated view, making it faster and easier for security teams to uncover and remediate threats. While EDR may be able to collect a large volume of data, it often takes XDR to parse this information, and translate it into actionable insights.
EDR vs XDR
Gartner coined the term Endpoint Detection & Response (EDR) in 2013, to describe security technology designed to protect end users and endpoints from attacks that bypassed traditional antivirus defenses. If a security team is interested in XDR vs EDR, the main difference is that XDR takes a broader approach to cybersecurity, also covering data from endpoints, but including cloud environments and the wider network. EDR is a predecessor to XDR; XDR takes protection and response much further.
XDR and MDR
In 2016, Gartner introduced the idea of Managed Detection & Response (MDR). This enhanced the approach of using traditional Managed Security Service Providers (MSSPs) who usually worked in a reactive and alert-driven way. Instead, MDR describes a proactive approach to cybersecurity, including threat hunting, and containment beyond notification. Similar to the way XDR enhances EDR to take a broader view of the whole IT environment, eXtended Managed Detection & Response (XMDR) takes MDR to the next level.
Why do enterprises need XDR security?
Due to the connected nature of today’s environments, XDR security is a critical element of any modern enterprise strategy for preventing data breaches and cyberattacks. With the rise in cloud computing, and the advent of IoT and edge computing, it has become more complex than ever to visualize and protect IT environments. As XDR solutions consolidate data from multiple sources such as endpoints, security and network logs, and the cloud – security professionals are able to get a much broader and more complete view.
What is driving adoption of XDR?
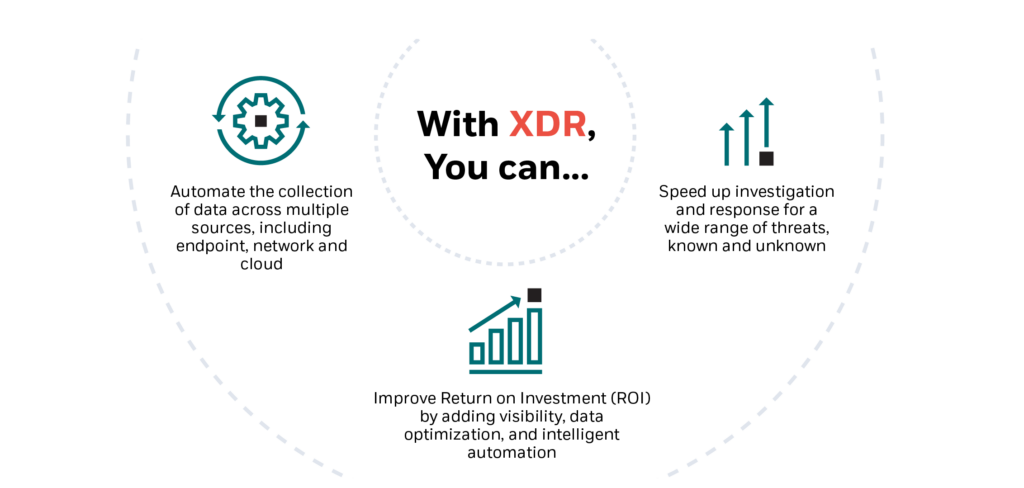
As well as the need to secure the cloud and new connected areas of the business, XDR is gaining in popularity because of its ability to add automation and control to an organization’s security posture. Security teams can respond a lot faster to incoming threats when all of their data is being aggregated and consolidated from multiple, previously siloed sources.
What problems does XDR solve?
EDR solutions focus on the endpoint, and for good reason. Attacks often target endpoints, as humans are often the weakest link in any environment. From an infected endpoint, hackers can make lateral moves to other systems, such as applications, databases, and the cloud.
However, EDR alone isn’t enough. XDR extends visibility and protection to other telemetry, to help get a fuller picture of attacker behavior, and identify whether other areas have been breached or compromised. This is critical because attackers may achieve initial access and then lie dormant for weeks or months, waiting for their chance. When a change in permission occurs, or a vulnerability is found – they will take action, moving through the network unseen. XDR shines a light on these movements.
XDR also adds automation and visibility to MDR services, adding enhanced capabilities such as correlating data across a complex network and deploying real-time response, containment and mitigation.
How does XDR work?
XDR is a proactive method of threat detection and response which provides a wide view of all data, from endpoint and network, to cloud. It applies automation and intelligence to identify hidden and sophisticated attack methods ahead of time, and can track risk across the organization, no matter where it originates.
There are three separate elements to how XDR solutions work.
- First, all the data is gathered from various places across the IT environment. These large volumes of data need to be consolidated and normalized, usually with the help of automation.
- Second, the data is analyzed and parsed to support security teams in detecting threats.
- Finally, response processes vary between different XDR examples, but security teams will prioritize actions and create a strategy for containment and recovery.
What is Managed XDR?
Managed XDR (MXDR) is an approach where a security team outsources XDR support to a knowledgeable and expert partner. This allows companies to benefit from automation and the human touch, both of which are critical to keeping an IT environment secure.
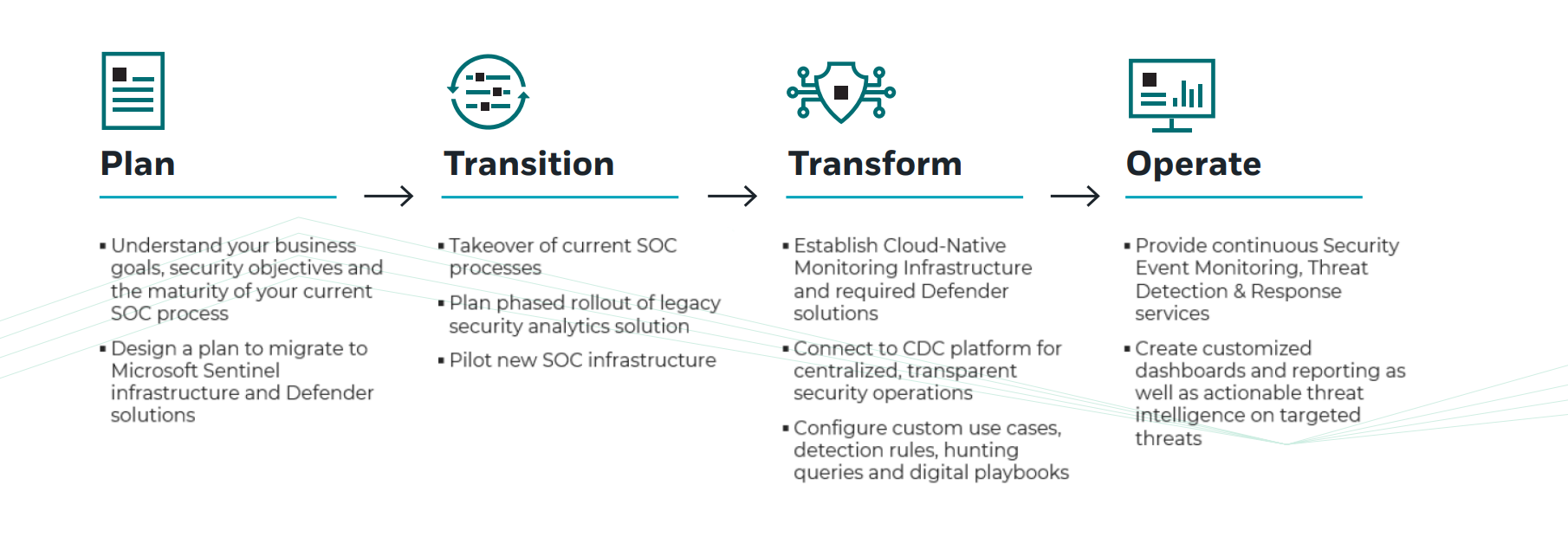
One example of managed XDR monitoring and protection we offer at CyberProof is Microsoft XDR managed services. The CyberProof Defense Center (CDC) platform integrates with Microsoft Sentinel and Microsoft 365 E5, and provides a single consolidated interface to support threat detection and response. We support teams in setting up and configuring Microsoft Defender Suite, and protecting an entire IT environment – from endpoints, to applications identities and the cloud.
What are the key elements to look for in an XDR solution?
XDR products come in many shapes and sizes, but there are a few main value-adds that a business should aim to cover when choosing XDR cybersecurity solutions.
- Extended visibility: XDR platforms should maximize visibility across on-premises and cloud environments, including the data that moves from one to the other, and cloud identities and multi-cloud environments, too.
- Data optimization: Cloud-native XDR tools should enhance log collection, data parsing, tagging, and filtering of relevant security data. Managed XDR can support security teams in creating a continuous process for collecting new data sources.
- Automation: The right XDR technology allows for automation of repeatable, low-hanging fruits, such as patching and testing enterprise systems, infrastructure improvements, and creating reports and auto-replies to employees.
- Infrastructure as Code (IAC): Use Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines to keep content up to date, including threat hunting queries, automation rules, and more. Major modifications can happen in real-time.
Key benefits of XDR when organizations take a managed approach
There are many reasons to implement XDR in a business environment. Here are some of the top benefits of a managed approach to XDR:
- Move from reactive response to proactive threat hunting: Managed XDR allows teams to search for known threats, investigate more thoroughly during incident response, and perform continuous behavior analysis from a large volume of data as it is generated.
- Implement best practices: MXDR teams do this every day. They leverage best practices such as the MITRE ATT&CK matrix, and have access to threat intelligence gathered from the clear, deep and dark web.
- Depth and breadth of visibility: Teams can leverage security logs alongside non-security related data, and be alerted to information that would have been missed by traditional security controls.
What should customers look for in an XDR solution?
One of the main considerations when choosing an XDR partner is how they manage large volumes of data. At CyberProof, we have our own CyberProof Log Collector to help clients reduce costs and resource investment. The platform parses, tags and normalizes all data before it enters our cloud data lake, locally deployed and able to ingest terabytes of data.
Security teams can ask their provider questions such as:
- How will you pull data from multiple sources at scale?
- What processes do you have for reducing costs and time to value?
- Do you have any gaps in data visibility – or can you cover network, endpoint, cloud, OT, and IoT information?
Mistakes to avoid with XDR platforms
Collecting data and detecting threats is only step one. Certain XDR platforms will put most of their emphasis on the Detection element, and offer a subpar solution when it comes to Response.
For effective response, teams need to be able to coordinate their information, offering a variety of response actions. Best practices for success include documented playbooks which cover common and possible incident scenarios, clarity on who should take responsibility when it comes to containment and remediation, and a team ready with the expertise to perform deeper investigations.
How does XDR work with SIEM?
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) tools are also a critical element of any security arsenal. Many people think that they need to make a decision about XDR vs SIEM, but in reality – companies need them both.
SIEM collects and integrates a lot of different log sources, such as infrastructure components, cloud environments and application logs. In contrast, XDR collects in-depth data from endpoints, cloud, security logs, and the network. XDR will go further than collecting data, and also analyze behavioral activity, and add deeper behind the scenes analysis to the picture, to find malicious usage of any components. SIEM may be able to detect threats, but an XDR can respond to threats, too.
The two technologies complement one another, and so integrating SIEM data into an XDR provides the greatest level of protection.
SOC challenges - How to address them with a managed approach
When implementing an XDR solution, there are three key challenges that today’s SOC teams face, which also impact the wider business.
- Complexity: Implementing XDR will touch many elements of the business, and requires thorough planning and careful execution to build and manage the platform moving forward.
- Cost: The information generated by XDR is vast, and all the data it touches needs to be analyzed and parsed to uncover insights. This can use a lot of resources, and end up being costly for an organization.
- Skills: Handling XDR involves a lot of niche skills. Teams need to have expertise in cloud, networking, endpoints, and threat hunting and intelligence. Most tools don’t work out of the box, and need configuration to suit business context.
A managed approach to XDR means you have a predictable Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), and can leverage the highest level of expertise to proactively secure your organization, without adding headcount or resource investment. As the implementation and ongoing maintenance is outsourced to a team that implements these solutions every day, the complexity is no longer your concern.
If you’re thinking about implementing XDR, and are interested in a managed approach, download our Managed XDR datasheet

Frequently asked questions
What does XDR mean?
XDR stands for eXtended Detection & Response. It is a security strategy that works to monitor a wide range of data sources to identify and mitigate risk. It has evolved from Endpoint Detection & Response (EDR) and Network Detection & Response (NDR) to encompass greater amounts of information about today’s connected environments.
What is XDR and how does it work?
eXtended Detection & Response works in three discrete stages. First, data is collected from a wide range of sources, from endpoints and network logs, to security event logs, SIEM SOAR and the cloud. The data is then analyzed to support security teams in uncovering existing and potential threats. Security teams then implement mitigation strategies and incident response to improve the environment’s security posture.
What is the difference between XDR and EDR?
While Endpoint Detection & Response (EDR) focuses on the endpoint and the end user, eXtended Detection & Response (XDR) pulls information from a wider range of sources, including the wider network and the cloud. Cloud-native XDR can help security teams to act faster and visualize the whole IT environment in one single, consolidated view.
What is XDR vs Siem?
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) gathers and consolidates a wide range of log sources from the cloud, applications, and the infrastructure itself. XDR also collects data, but it’s not an either/or. XDR can be enhanced with information from SIEM technology, and as SIEM does not perform behavioral analysis, automation or containment processes - it is not enough on its own without XDR capabilities.
What is the difference between MDR, XDR, and EDR?
MDR stands for Managed Detection & Response. This is the process of outsourcing security measures to an expert partner who can implement automation, extended visibility, data optimization and Infrastructure as Code (IaC) on your behalf. While many Endpoint Detection & Response or eXtended Detection & Response platforms are intended to be deployed in-house, which incurs high costs and complexity, and requires high skill level to manage, MDR allows organizations to outsource - and to gain XDR and EDR benefits, without the overheads.

Speak with an expert
Explore how CyberProof can help you anticipate, prevent, and mitigate ever-evolving cyberattacks in hybrid and cloud-native environments.
SPEAK WITH AN EXPERT