As you know, October is Cybersecurity Awareness Month, a time when we focus on securing the digital habits and technologies that power our lives. But this year, the conversation needs to move beyond strong passwords and basic phishing training. This year, CyberProof will share a series of blogs on some of the top cyber topics during the month of October that dives into these trends and best practices.
Our first topic in the series is Artificial Intelligence (AI). For years, AI has been hailed as the ultimate productivity booster—your company’s new, brilliant assistant. But while your teams are innovating with generative AI, a silent, sophisticated war is being waged against it. Adversaries are no longer content with just stealing passwords; they are actively probing, tricking, and hijacking your AI models to leak sensitive data, spread misinformation, and create an entirely new class of backdoor into your organization.
Just as hackers flocked to the Cloud and IoT devices in previous eras, AI systems are now the newest, most vulnerable playground. This is not a threat of the future—it’s an incident happening right now. This post will pull back the curtain on why hackers love AI, walk you through recent real-world attacks, and give you the essential playbook for defending your models before it’s too late.
AI – The New Attack Surface
Imagine your organization build a powerful AI assistant to boost your company’s productivity. Employees would be extremely happy to use it on their daily tasks. But do you know attackers are quietly probing it. Adversaries are not limited to steal passwords; they are targeting your AI model itself by tricking it into leaking sensitive information or even hijacking you model to spread misinformation. This is not something to be happened in the future, it’s already an incident right now.
AI is no longer a fancy tool. It is one of the major contributors in making decisions, automating workflows and of course handling sensitive information. But here arises the security concern. Do AI open the door to a new attack surface? As we know, the past milestone technologies like IoT and cloud being targeted by hackers, AI is the new playground for adversaries to target before organizations secure it.
Why Hackers Love AI
Hackers see AI not as a breakthrough for society but as a fresh, vulnerable playground. Unlike traditional computer systems, AI models are still experimental and deployed without proper security defence measures. For hackers, this is a golden opportunity. Using techniques like prompt injection, they can mislead the AI model revealing sensitive information, data exfiltration and even misuse it for malicious intentions.
Once an attacker finds out how an AI model responds, it is easy for them to replicate the same exploit across countless systems using automation. By this way they can use every insecure AI deployment as potential backdoor. In the eyes of hackers AI is not just a target, it’s the perfect low – cost, high-reward opportunity.
In real world we could see AI models being directly targeted by adversaries. Let’s walk through a few incidents:
AI Browser Extensions
The number of AI powered browser extensions for content summarization is being rapidly increasing. As per chrome-stats[.]com, approximately 40 AI powered chrome extensions have appeared this year. These Chrome extensions were downloaded by thousands of users across the world. This gives an easy opportunity for threat actors to get sensitive information from unsuspecting users.
When installing an AI powered extension, it requests broad host permissions that allow it to read the DOM/ page content of any site the user visits (including your Gmail, WhatsApp web, Outlook etc) for summarization. By the way it could read email subjects, bodies, chat history, messages etc. This scrapped data is sent to these extension’s AI model for processing, but malicious or vulnerable models can forward it anywhere. On an intel released by Unit42, those chrome extensions forward user’s data from WhatsApp and Gmail silently to low reputed websites like:
- askyumawebapp.fly[.]dev
- gosupersonic[.]email
Here are (2) indicators published by Unit42.
Chrome browser extension IDs:
- eebihieclccoidddmjcencomodomdoei – Supersonic AI
- fahgecbhaoedbchcmhakmjbfbfhgjmbl – WhatsApp Message Summary
Malicious Models in Repositories
Researchers at JFrog and others found that some AI models uploaded to Hugging Face, a platform and open-source community used to build, share, and use machine learning (ML) and natural language processing (NLP) models contained malicious code hidden in model files. These backdoored models could execute arbitrary code when loaded, effectively giving adversaries a way to compromise developer systems or downstream apps.
Chatbot Exploitation
Lena AI, the ChatGPT-powered chatbot featured on Lenovo’s website, was shown to be exploitable by the researchers. Attackers could inject malicious HTML/JS via user queries. This turned the chatbot into a delivery vector for cross-site scripting (XSS) and potential backdoors.
Prompt Injection & Tokenization Evasion (Token Break)
Researchers from HiddenLayer uncovered an LLM attack called TokenBreaker which targets LLM input processing. By slightly altering words (e.g., “instructions” → “finstructions”), they can bypass AI safety filters. While not corrupting the model weights, this directly exploits the model’s tokenization pipeline to force unsafe outputs.
Model Corruption via Hardware Exploit (GPUHammer)
Researchers demonstrated GPUHammer, a Rowhammer-style attack against Nvidia GPUs (GDDR6 memory). By flipping bits in GPU memory, attackers silently corrupted AI model parameters, reducing model accuracy from 80% to 0.1%. This shows adversaries could target deployed models by exploiting hardware-level flaws in inference servers.
The Top 5 AI Threats in 2025
| Threat | What It Does | Business Impact | Real-World Example |
| Prompt Injection & Jailbreaks | Malicious inputs trick AI into bypassing rules or leaking data. | Data leaks, compliance violations, brand damage. | Hidden prompts in documents cause AI copilots to exfiltrate customer info. |
| Data Poisoning & Malicious Models | Attackers inject poisoned data or distribute backdoored models. | Corrupted decisions, hidden backdoors, insider risk. | Poisoned AI model in Hugging Face repo downloads remote code. |
| Model Theft & Extraction Attacks | Repeated queries replicate proprietary model behavior. | Loss of IP, competitor advantage, cloned services. | LLM copied through “model inversion” by adversarial queries. |
| Adversarial & Evasion Attacks | Inputs crafted to fool models or bypass filters. | Security bypass, fraud, deepfake amplification. | Modified phishing emails that evade AI spam filters. |
| Supply Chain & Infrastructure Attacks | Targeting datasets, dependencies, GPUs, or AI plugins. | Mass compromise at scale, systemic business risk. | GPUHammer attack flips model weights; malicious NPM package poisons AI pipeline. |
Defender’s Cheat Book
As AI becomes more integral to various industries; it introduces new attack surfaces and vulnerabilities that traditional cybersecurity frameworks aren’t designed to handle. In 2021 MITRE released ATLAS (Adversarial Theft Landscape for Artificial Intelligence Systems) foreseeing the upcoming security challenges that AI brings to an enterprise. MITRE ATLAS is an evolving knowledge database of adversary tactics and techniques targeting AI systems.
Defending against AI threats requires a layered approach that combines proactive testing, supply chain assurance, runtime monitoring, and strict governance. Organizations should begin by continuously red teaming their models using frameworks like MITRE ATLAS to simulate real-world adversarial attacks. At the same time, supply chain security is critical from securing datasets and training pipelines to validating third-party models and dependencies.
Once deployed, AI systems need runtime monitoring to detect prompt injections, jailbreak attempts, and data leakage in real time. Finally, governance provides the guardrails that keep AI safe, ensuring alignment with compliance requirements and ethical standards. Taken together, these strategies form a practical playbook for securing AI in production.
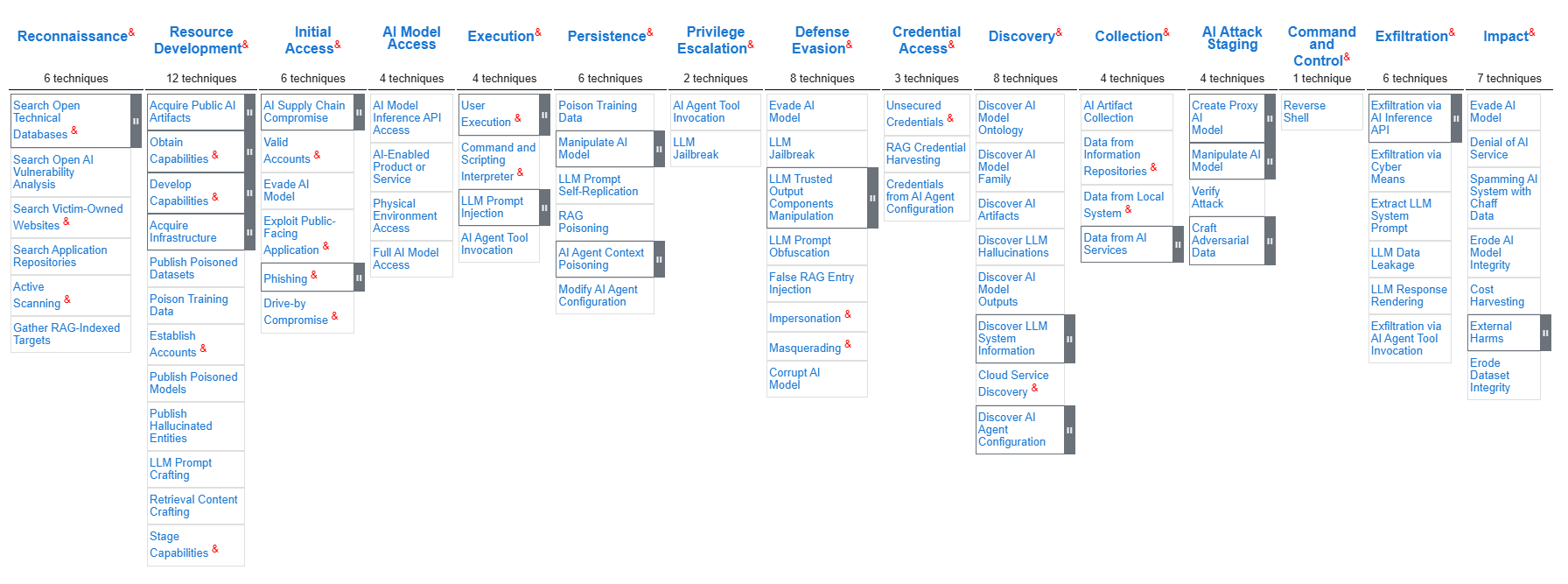
(source: https://atlas.mitre.org/matrices/ATLAS)
Fig. 1: MITRE Atlas Matrix
Recommended Actions
The reality is clear: AI insecurity equals business insecurity. Attackers don’t need to compromise your firewalls if they can exploit your models, and they don’t need to phish your employees if they can manipulate your AI agents.
Our recommended actions for maintaining AI supply chain integrity include:
- Secure the AI supply chain (models, datasets, dependencies).
- Deploy guardrails and firewalls to block prompt injections and unsafe outputs.
- Continuously red team the models using frameworks like MITRE ATLAS.
- Monitor AI systems at runtime just as rigorously as they monitor networks.
Why This Matters for CISOs & Executives
For executives, AI security is no longer a technical afterthought it’s a boardroom priority. AI models are increasingly embedded into decision-making processes, customer interactions, and even security operations. A compromised model doesn’t just represent a technical failure; it challenges trust, exposes sensitive data, and creates security risk.
CISOs must recognize that every AI deployment is an expansion of the organization’s attack surface. By embedding AI security into enterprise risk management strategies, leaders can ensure innovation does not come at the expense of resilience. In short, securing AI is about securing the future competitiveness and integrity of the business.
The companies that win in the age of generative AI won’t just be the ones that adopt AI fastest—they’ll be the ones that secure it best. By integrating AI-enhanced SOC capabilities and prioritizing a multi-layered defense strategy, businesses can better protect themselves from the increasing sophistication of cyber threats. Investing in AI-driven SOCs and leveraging CyberProof’s solutions, businesses can strengthen their security and protect themselves more effectively from the increasing sophistication of cyber threats. AI is no longer the future. Secure it today.